Laser cutting is the use of a focused high power density laser beam to irradiate the workpiece, so that the irradiated material quickly melt, vaporize or reach the ignition point, and at the same time with the beam coaxial high-speed air blowing molten material, so as to achieve the workpiece cutting, is one of the thermal cutting methods of cutting the workpiece.
It is divided into four categories: laser vaporization cutting, laser melting cutting, laser oxygen cutting and laser scribing and controlled fracture.
1) Laser vaporization cutting
Using a laser beam with high energy density to heat the workpiece, the temperature rises rapidly, reaching the boiling point of the material in a very short time, and the material begins to vaporize and form steam. The speed of these vapors is very high, and at the same time the vapor is emitted, a notch is formed in the material. The heat of vaporization of the material is generally large, so the laser vaporization cutting requires a large power and power density.
Laser vaporization cutting is mostly used for cutting extremely thin metal materials and non-metallic materials (such as paper, cloth, wood, plastic and rubber, etc.).
2) Laser melting cutting
When laser melting cutting, the metal material is melted by laser heating, and then non-oxidizing gas (Ar, He, N, etc.) is sprayed through the nozzle coaxial with the beam, and the liquid metal is discharged by the strong pressure of the gas to form the incision. Laser melting cutting does not require the metal to be completely vaporized, and the energy required is only 1/10 of that of vaporized cutting.
Laser melting cutting is mainly used for the cutting of some non-oxidizing materials or active metals, such as stainless steel, titanium, aluminum and its alloys.
3) Laser oxygen cutting
The principle of laser oxygen cutting is similar to oxy-acetylene cutting. It uses a laser as a preheating heat source and an active gas such as oxygen as a cutting gas. On the one hand, the gas blown out interacts with the cutting metal to undergo oxidation reaction and release a large amount of oxidation heat; On the other hand, the molten oxide and melt are blown out of the reaction zone, forming a notch in the metal. Due to the oxidation reaction in the cutting process produces a lot of heat, so the energy required for laser oxygen cutting is only 1/2 of the melting cutting, and the cutting speed is much greater than the laser vaporization cutting and melting cutting. Laser oxygen cutting is mainly used for carbon steel, titanium steel and heat-treated steel and other easily oxidized metal materials.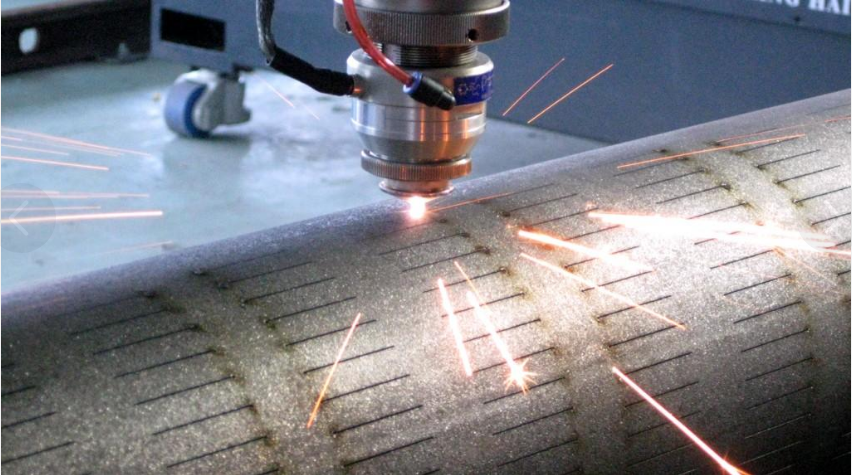
4) Laser scribing and controlled fracture
Laser scribing is the use of high energy density laser scanning on the surface of the brittle material, so that the material is heated to evaporate out of a small slot, and then apply a certain pressure, the brittle material will be split along the small slot. The lasers used for laser scribing are generally Q-switched lasers and CO2 lasers.
Controlled fracture is the use of the steep temperature distribution generated by laser grooving to create local thermal stress in the brittle material, causing the material to break along the small grooves.
Post time: Nov-30-2023
